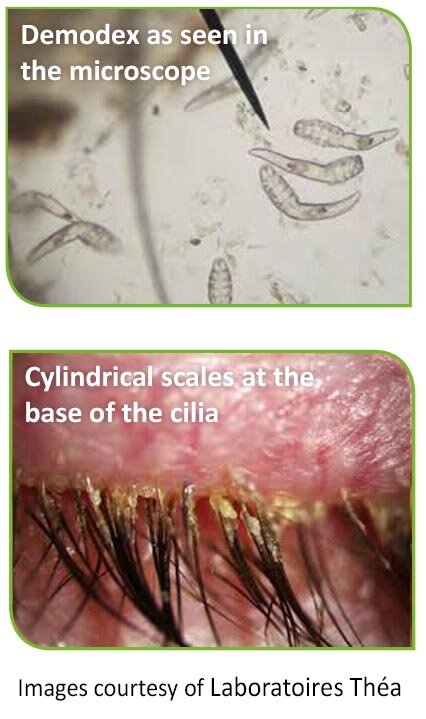
Could microscopic creatures living on your skin be the root cause of persistent skin irritation and eye problems? Despite their minuscule size, Demodex mites can significantly impact human health. These tiny arachnids, barely visible to the naked eye, inhabit hair follicles and sebaceous glands, primarily around the face, eyelashes, and eyebrows. While they are typically harmless, an overpopulation or infection caused by these mites can lead to a range of distressing symptoms, including redness, dryness, itching, and even loss of eyelashes.
Demodex mites are naturally present on most human bodies, with two primary species affecting humans: Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. The former resides in hair follicles, while the latter burrows deeper into sebaceous glands. When their population spirals out of control, they can cause conditions such as blepharitis, rosacea, and demodicosis. Blepharitis, characterized by inflamed eyelids, is particularly troublesome for those afflicted. Symptoms include eyelid irritation, crustiness, and discomfort, often exacerbated by the mites' lifecycle, which involves feeding, reproducing, and eventually dying within the follicles.
| Bio Data | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Dr. Kathryn Najafi-Tagol |
| Profession: | Ophthalmologist |
| Designation: | Founder and Medical Director |
| Institution: | Eye Institute of Marin |
| Field of Expertise: | Treatment of ocular surface diseases, including Demodex-related issues |
The die-off reaction of Demodex mites after treatment can sometimes confuse patients. As these mites perish during therapy, the body may react to their decomposition, leading to temporary worsening of symptoms before improvement occurs. This phase is crucial in understanding the healing process, especially in cases involving mange in dogs, where similar reactions occur. For instance, when treating demodectic mange in canines, veterinarians often observe an initial flare-up due to the inflammatory response triggered by dead mites.
Rodent and bird mites may also bite humans when their original hosts die or abandon nests. Among rodent mites, the house mouse mite is notorious for biting people. Such occurrences highlight the importance of maintaining cleanliness and addressing infestations promptly to prevent cross-species transmission. Additionally, understanding the behavior and lifecycle of these mites aids in devising effective strategies to manage them.
Symptoms of Demodex mite infestation extend beyond mere skin irritation. They encompass a spectrum of manifestations, from mild discomfort to severe complications. Individuals might experience redness, dryness, scaling along hair follicles, papules, pustules, and rough texture on the skin. In severe cases, this condition could contribute to the development of rosacea, a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting facial skin. Moreover, eyelash mites, specifically Demodex folliculorum, can lead to blepharitis, causing inflammation, itchiness, and potential loss of eyelashes.
New approaches for combating Demodex mites involve advanced diagnostic techniques and targeted treatments. Ophthalmologists and optometrists worldwide recognize the challenge posed by these mites in routine patient care. Dr. Kathryn Najafi-Tagol, founder and medical director of the Eye Institute of Marin, emphasizes the necessity of adopting innovative methods to tackle this issue effectively. Her clinic specializes in treating ocular surface diseases, including those linked to Demodex infestations.
Treating Demodex-related conditions requires a multifaceted approach. Topical medications, oral antibiotics, and mechanical cleaning procedures form the cornerstone of therapy. Cliradex, a natural product derived from tea tree oil, has gained popularity for its efficacy in managing Demodex blepharitis. By reducing the mite population and alleviating associated symptoms, it offers relief to many sufferers. Furthermore, incorporating lifestyle changes such as improved hygiene practices and dietary modifications can complement medical interventions.
Eyelash mites, though ubiquitous, become problematic only when their numbers increase disproportionately. Identifying signs early and seeking professional help promptly ensures timely management and prevention of complications. Awareness about these mites and their potential impact on health empowers individuals to take proactive measures against infestations. Understanding the nuances of Demodex mites—how they thrive, multiply, and affect different parts of the body—is essential for developing comprehensive treatment plans.
In conclusion, addressing Demodex mite infestations necessitates a holistic approach combining medical expertise, patient education, and adherence to treatment protocols. Whether dealing with skin irritations or ocular disorders, recognizing the role played by these minuscule organisms is vital for achieving optimal health outcomes. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment modalities, healthcare providers continue striving toward better solutions for managing Demodex-related conditions.
| Information Related to Topic | |
|---|---|
| Common Species Affecting Humans: | Demodex folliculorum, Demodex brevis |
| Primary Locations: | Face, Eyelashes, Eyebrows |
| Associated Conditions: | Blepharitis, Rosacea, Demodicosis |
| Treatment Options: | Topical Medications, Oral Antibiotics, Mechanical Cleaning |